Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting has become crucial for companies globally, especially in India, where regulatory pressures are mounting. According to a report by PwC, by 2023, over 50% of Indian businesses had pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2030.
Effectively reporting on these criteria is more important than ever, both for regulatory compliance and for meeting the growing demands from stakeholders and investors. A survey conducted by Gartner found that 85% of institutional investors take ESG factors into account when making investment decisions.
As the Indian government mandates, transparency in reporting, requiring companies to disclose critical data on emissions, energy consumption, waste management, and water usage, further increasing the urgency for precise ESG metrics.
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force in this domain, enabling organizations to gather, analyze, and report data that supports their sustainability initiatives. This blog explores how IoT technology enhances ESG reporting through accurate data collection and analysis.
Table of Contents
ToggleImportance and Regulations
By late 2023, the Indian government had made substantial strides in mandating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting among companies. These regulations require organizations to systematically gather, analyze, and transparently disclose their ESG data.
In India, several frameworks and guidelines have been introduced for ESG reporting. However, these frameworks vary widely in their requirements and focus areas, leading to confusion and inconsistency in ESG reporting.
Some of the regulations and guidelines shaping ESG reporting in India include:
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): SEBI has mandated that the top 1,000 listed companies disclose their sustainability initiatives through a comprehensive Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR).
- Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA): GRIHA is India’s national rating system for green buildings, administered by the Energy and Resources Institute (TERI). It assesses buildings based on various sustainability criteria, including site selection, water and energy utilization, material use, and indoor environmental quality.
- Indian Green Building Council (IGBC): It has developed multiple rating systems tailored to different types of buildings—residential, commercial, and institutional. The IGBC’s Green Building Certification assists developers and architects in integrating sustainable practices, such as efficient resource usage, waste reduction, and enhancing indoor environmental quality.
Together, these regulations and initiatives reflect a comprehensive effort to embed sustainability into the core operations of businesses in India, fostering a culture of accountability and transparency in ESG reporting.
Challenges in ESG Reporting
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting is crucial for companies aiming to demonstrate transparency and responsibility in their operations. However, there are several challenges that organizations encounter in this process
Data Availability and Quality
Accurate data collection is vital for effective ESG reporting. Organizations often struggle to obtain necessary data, especially regarding social and environmental impacts, due to data silos, lack of clarity, or unavailability. Ensuring the quality of this data is crucial, as inaccuracies can result in misreporting and affect business decisions.
Lack of Centralized Visibility
The absence of a centralized dashboard inhibits organizations from gaining a comprehensive view of their sustainability efforts. Without consolidated data, it becomes challenging to track progress, identify gaps, and make informed decisions.
Manual Data Collection
Many organizations still use methods like spreadsheets and paper systems that are susceptible to human error, such as data entry mistakes or misinterpretation of metrics. Inconsistencies can occur when different departments use varying definitions and methodologies for similar metrics. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, undermining ESG report reliability.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment surrounding ESG reporting is rapidly evolving, with new guidelines and requirements continuously emerging. Organizations must stay abreast of changes, which can vary significantly by jurisdiction. Traditional systems may struggle to keep up with these changes, leading to increased risk of non-compliance and potential penalties.
How Zenatix can help organizations automate ESG Reporting
Zenatix by Schneider Electric specializes in integrating Internet of Things (IoT) technology to streamline ESG reporting and enhance sustainability initiatives for organizations. By leveraging advanced IoT solutions, Zenatix provides comprehensive tools for energy management, water management, and carbon emissions tracking, enabling companies to automate ESG reporting.
Energy Consumption Monitoring
Through sub-metering, Zenatix provides insights into energy consumption across key systems like Diesel Generators (DG), Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC), and solar panels. This comprehensive view allows organizations to optimize energy usage effectively.
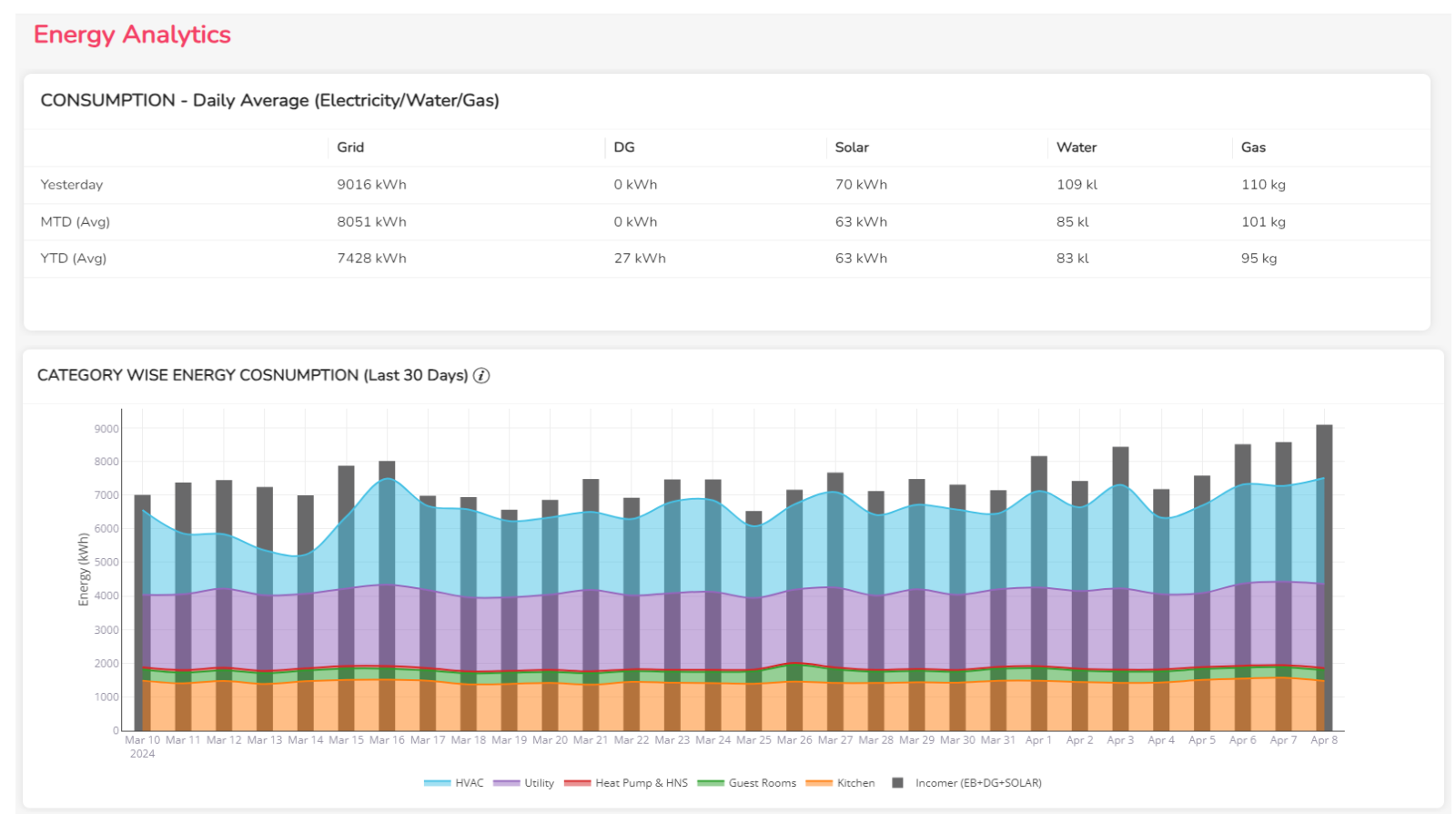 Compliance Benefits
Compliance Benefits
- Automated Energy Reporting: Zenatix generates Year-over-Year Energy Consumption Reports to help organizations comply with regulatory requirements and achieve internal benchmarks.
Value-Added Benefits
- Accurate Tracking of Energy Consumption: With precise monitoring, organizations can identify inefficiencies and implement targeted interventions.
- Benchmarking: Tracking consumption at the mains and HVAC levels enhances operational efficiencies and fosters accountability.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By utilizing data insights, organizations can significantly reduce energy waste, contributing to sustainability objectives.
Water Consumption Monitoring
Zenatix leverages water usage data to help organizations detect leaks and promote conservation efforts.
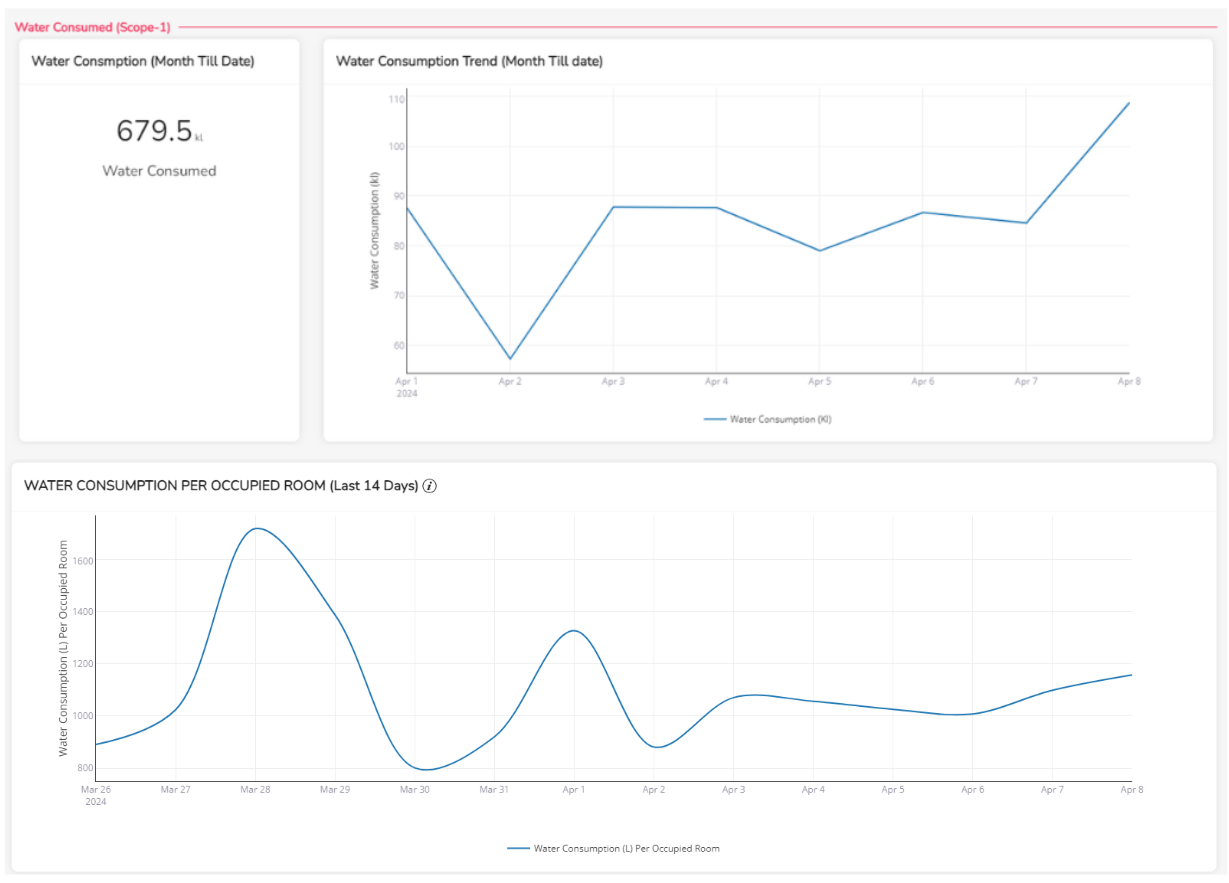 Compliance Benefits
Compliance Benefits
- Year-over-Year Total Water Consumption Reports: The platform provides Year-over-Year Total Water Consumption Reports, ensuring compliance with sustainability reporting requirements.
Value-Added Benefits
- Reduced Water Bills: By tracking and optimizing water consumption, organizations can lower operational costs and support resource conservation.
- Benchmarking Across Sites: Organizations can compare water usage across different facilities to identify best practices and areas for improvement.
- Decreased Energy Consumption by Pumps: Optimizing water management reduces the energy required for pumping, further enhancing sustainability.
Carbon Emissions Tracking
Zenatix offers comprehensive tracking of carbon emissions from various sources, including grid operations and Diesel Generator (DG) systems.
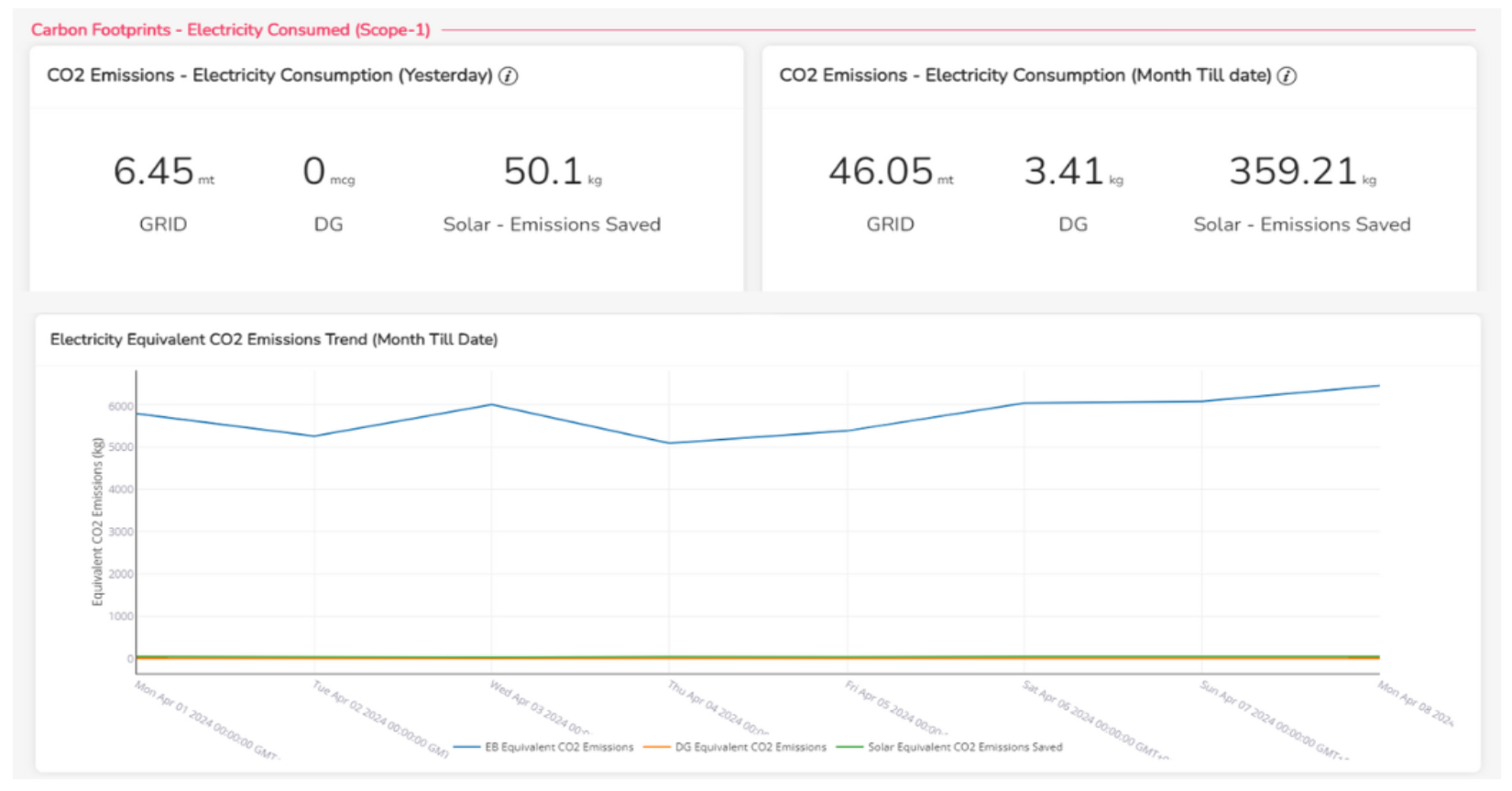 Compliance Benefits
Compliance Benefits
- Year-over-Year Carbon Emission Reports: Zenatix generates detailed carbon footprint reports, aligning with regulatory demands and sustainability targets.
Value-Added Benefits
- Equipment-Level Emissions Data: Zenatix provides detailed insights into emissions by specific equipment, enabling targeted interventions.
- Real-Time Alerts for Excessive Emissions: Instant notifications help organizations respond quickly to emissions spikes, ensuring compliance and enhancing overall sustainability efforts.
Conclusion
By partnering with Zenatix, organizations can leverage IoT technology to transform their ESG reporting processes and sustainability initiatives. The benefits extend beyond compliance, offering valuable insights that drive operational efficiencies, reduce costs, and enhance corporate responsibility. Zenatix helps organizations not only meet but exceed their ESG goals, positioning them as leaders in sustainability within their industries.
